
Autism spectrum disorder (ASD), popularly known as autism, is a group of neurodevelopment disorders which involves problems with social communication, repetitive behaviour, and restricted interests. It’s a complicated condition. The set of strengths and weaknesses in autistic folks varies from person to person. Now, let’s start with the introduction part.
Autism is a condition that is invisible or hidden. An autistic person may exhibit behavioural patterns and certain modes of communication, but these are not universal because every autistic person is unique. As a condition, it starts affecting how an individual communicates and how they start perceiving their surroundings. It is also classified as a spectrum disorder. However people diagnosed with autism have certain characteristics in common, but their behavioural pattern is very different from each other. This condition does not run from high to low, but it rather varies, just like how one person differs from another. Some autistic persons are capable of living independently, whereas some may face more difficulties. For example, some autistic individuals suffer from cognitive impairment, which implies that their support requirements may vary. In this article, we will learn about symptoms, causes, treatment, risk factors, tests, and the role of cow cuddling therapy in the effective treatment of this disorder.
Autism, also regarded as Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD)[1], is a development-related disorder which is caused by brain differences. ASD patients may have known differences, like genetic conditions. However, other causes are still unknown. Some scientists believe that numerous causes of this neurodevelopment disorder tend to interact and alter how humans develop. Researchers still have a great deal to learn about all of these factors that cause this developmental disability and how these causes can affect human behaviour. Individuals diagnosed with ASD might interact, communicate, behave, and learn differently than most people. Often there is very little about the appearances that distinguish them from others. Individuals diagnosed with autism have a wide range of abilities. For example, several individuals diagnosed with this complicated condition require a lot of assistance in their everyday lives, whereas some can live and work with minimal to no assistance.
Young adults and adolescents with ASD might struggle to keep and make friends, communicate with adults and peers, or even what is appropriate behaviour to maintain at school or in the workplace. Medical professionals might also be able to know this if an individual suffering from this neurodevelopment disorder also has disorders like hyperactive disorder, depression, or anxiety. ASD is usually manifested before the age of 3 and may persist for a person’s entire life; symptoms occasionally get better with age. Autism symptoms can appear in some kids within the first year whereas, others might not experience symptoms until they are 2 years old or more. In some cases, children diagnosed with ASD can reach developmental milestones and start developing new skills up until the age of 18-24 months. At this point, they gradually lose the abilities they previously possessed or stop developing new skills.
The symptoms of autism spectrum disorder have a negative impact on communication and language comprehension and development. These impacts further lead to rippling effects on various aspects of functioning, such as peer interactions and academic progress. The adage, “if you have met one individual with ASD, you have only met one person with this disorder”, is true. Different people make experience different symptoms.
Listed below are a few widespread symptoms characterized into two categories:
Listed below are a few symptoms related to social communication and interaction skills characteristics which can be found in autistic individuals:
Autism differs from disorders that are only characterised by communication and social interaction issues by virtue of these behaviours. A few symptoms of repetitive or restrictive Autism behaviour are:
Other symptoms visible in autistic persons are showcased below:
The cause of autism spectrum disorder is unknown. There are probably numerous causes, given the disorder’s complex nature as well as the fact that severity and symptoms vary. Environmental and genetic factors may lead to ASD.
The National Institute of Neurological Disorders & Stroke has claimed that an individual’s propensity for this spectrum disorder is influenced by both environment and genetics. But various sources, both new and old, have come to the conclusion that vaccines do not cause this complicated disorder.
A highly controversial study from 1998 suggested a connection between the MMR vaccine (rubella, mumps, and measles) and autism. But later, in 2010, that study was revoked after being refuted by thorough studies.
Genetics
Autism appears to be caused by many genetic variations. For some kids, genetic conditions like fragile X syndrome or Rett syndrome may be linked to autism. Other children may be more susceptible to ASD because of genetic variations (mutations). Numerous different genes may influence how the brain develops, how brains communicate, or even how severe a symptom is. Although some genetic changes appear to be descended, others happen on their own. Many such gene differences may be passed on to an infant if one or both parents possess them. Sometimes, early embryos or even the reproductive cells and/or eggs combine to make the embryo experience such gene mutations on its own. Once again, the large percentage of such gene alterations doesn’t really result in ASD. They merely increase the risk.
Environmental Factor
Currently, scientists are examining whether bacterial diseases, birth complications, medications, and environmental toxins can cause autism spectrum disorder. According to research, people who are genetically predisposed to ASD may also be more vulnerable to certain environmental factors, which could either increase or decrease their risk.
Among the suspected autism risk factors are:
Youngsters diagnosed with autism and their families can greatly benefit from early diagnostic testing. However, determining an ASD diagnosis isn’t always an easy procedure; doctors instead depend on watching the behavioural pattern of children as well as listening and analysing parents’ complaints and worries, given that there is no lab test for this.
The symptoms of this neuro-related disorder are extremely varied. A few individuals who really are “on that spectrum” suffer from severe mental impairments. Some people are very smart and capable of living on their own. The first step in these two procedures to diagnose your child with ASD, no matter where they fall exactly on the spectrum, would be to take them to the paediatrician.
Listed below are three major tests which help in detecting autism:
Parents are asked to fill out this updated tool known as a modified checklist. This checklist assists in determining whether your child has a high, medium, or even low risk of having autism. There are about 20 questions on the test, which is also cost-free. Then, your child will undergo more diagnostic evaluation if the test results show a high risk of ASD. If the child has a medium risk, further enquiry is required to help categorize the results with the most certainty.
The team may include the following:

Various screening methods are used in this process. There are numerous options for developmental screening. However, ASD cannot be just diagnosed by using one single tool. Instead, a wide variety of tools and tests are conducted to make an accurate autism diagnosis.
Some of the examples of screening tools used in diagnosing autism:
Genetic tests cannot diagnose or identify autism, despite the fact that ASD is known to be a genetic condition. Both genetic and environmental factors play a very crucial role in the development of autism. Some researchers and scientists believed that to be an indicator of ASD. When anyone of such genetic tests yields a remarkable result, it is most likely that genetics did indeed play a role in the development of ASD.
Autism spectrum disorder does not have any known treatment that might work for everyone. The available treatment and therapies aim to improve the functioning of an autistic individual by minimizing the symptoms and fostering growth and development. An autistic child can learn critical functional, social, communication and behavioural skills with early intervention during the pre-school years.
An autistic individual’s needs might start changing from time to time, and the variety of school and home-based interventions and treatments can prove to be overwhelming. If your child has been diagnosed with medium or high-level ASD, make sure you keep in touch with a professional about treatment plans and therapies that might help in improving and comforting your child.
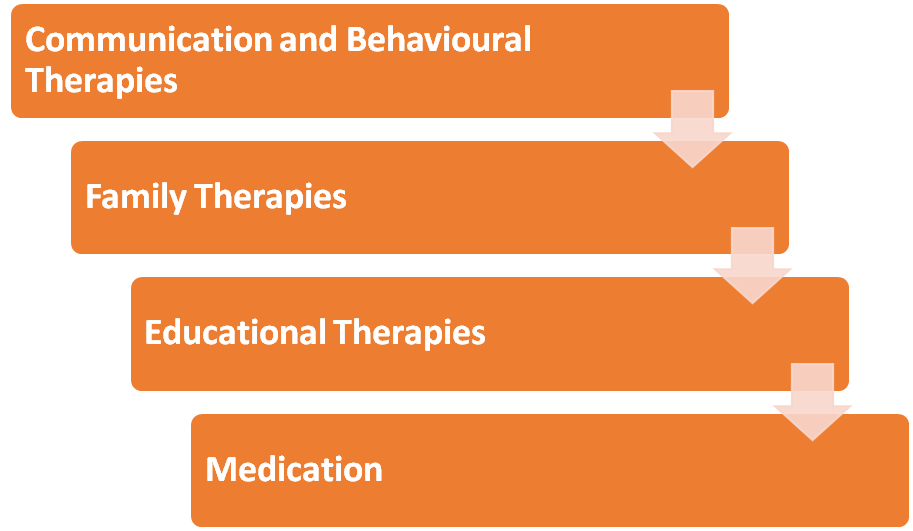
Listed below are a few effective treatment options for autism:
Role of Cow Cuddling Therapy
The practice of cow cuddling therapy is based on the natural therapeutic benefits of cuddling with an animal. Cow cuddling therapy has proven to encourage positivity and lower stress levels by releasing a hormone called Oxytocin in humans. This hormone is released during social bonding. Cuddling with large mammals like cows seems to enhance the calming impact of having an emotional support animal or a pet. Cow cuddling sessions usually begin by touring the farm area before spending desired hours resting and cuddling with a cow. Cuddling with a cow has province to be incredibly coming due to the animal’s warm body, enormous size, and slower heartbeat. Relaxing against a cow, giving the cow a back rub, and getting licked are all common parts of this therapeutic interaction.
You must be wondering how cow cuddling therapy can help treat autism. Autistic individuals carry low Oxytocin hormone levels in their bodies, contributing to social anxiety and stress. As mentioned above, cuddling a cow helps in releasing the Oxytocin hormone in the human body. Therefore, researchers started analysing the Oxytocin levels in autistic children to determine whether it plays a significant role in the development of autism or not. The results concluded that a low level of Oxytocin might cause social dysfunction and behavioural issues in autistic individuals. A study published by Yale University explains how Oxytocin nasal spray affected the social behaviour of an autistic child. They also claim that the therapy help in improving behaviour and social functioning. Other studies suggested that cow cuddling has been demonstrated as a therapy that encourages the production of Oxytocin hormone, leading to social interaction and behaviour improvement in autistic individuals.
Autism also known as an Autism spectrum disorder, is an ability caused by variations in the brain. An individual suffering from this health-related disorder frequently struggles with interaction and social communication. Additionally, autistic individuals also possess different ways of moving, learning, and even paying attention. In this article, we have mentioned all the necessary details related to autism and its treatment. As mentioned, cow cuddling therapy helps release the Oxytocin hormone, which aids in improving behaviour and social interaction in autistic individuals.
Read our Article: An Overview on Osteoporosis – Symptoms, Treatment and Causes
